Part 4: Adding Stateful Context to Your Agent
Our current system has one major limitation: it’s memoryless / stateless. Each conversation starts fresh, which means the AI can’t build on previous interactions or maintain context across multiple exchanges. Let’s fix that.
Think of this as giving our agent a notebook to remember what happened in previous messages. This enables much more sophisticated interactions where the AI can reference earlier parts of the conversation and build complex workflows over multiple steps.
You’ll learn how to:
We are following on from Part 3: Building Custom AI Tools in Laravel & React and the code from part 3 is available in the ai-agent-tutorial repository on GitHub.
Context model
The Context model serves as our agent’s memory system, storing conversation history across multiple interactions. Instead of treating each message as an isolated event, we can now maintain conversational context that allows the AI to:
- Reference previous messages and responses
- Build upon earlier tool executions
- Maintain workflow state across multiple requests
- Create more natural, contextual conversations
Here’s how it works: Each conversation gets assigned a unique UUID that groups related messages together. When a user sends a message, we’ll either create a new context (for new conversations) or append to an existing one. The AI can then see the full conversation history, including previous tool calls and their results, enabling much more sophisticated multi-step interactions.
For example, a user could say “Create a user named Alice”, followed by “Now find that user”, and the AI will remember the context from the first interaction to understand what “that user” refers to.
Create the Context model
Let’s create the Context model and migration (the -m flag creates the migration):
php artisan make:model Context -mThis creates the model (app/Models/Context.php) and migration (database/migrations/2025_07_21_000000_create_contexts_table.php):
You will noticce below the context model is very simple, it just has a messages field that is an array of messages. In a production application you would likely want to add more fields to the context model to store additional information about the conversation like the user who started the conversation, the date and time of the conversation, the AI model used, the temperature, etc.
Update app/Models/Context.php:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Concerns\HasUuids;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Context extends Model
{
use HasUuids;
protected $fillable = [
'messages',
];
protected $casts = [
'messages' => 'array',
];
}
Create the migration
Update database/migrations/2025_07_21_000000_create_contexts_table.php:
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
return new class extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*/
public function up(): void
{
Schema::create('contexts', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->uuid('id')->primary();
$table->json('messages')->nullable();
$table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*/
public function down(): void
{
Schema::dropIfExists('contexts');
}
};Run the migration:
php artisan migrateUpdating the ChatController to support persistent contexts
The updated ChatController introduces several important capabilities:
-
Context Creation: A new
newChatContext()method creates a unique chat session with its own UUID, allowing multiple concurrent conversations. -
Message History: Each context stores the complete conversation history in a JSON field, preserving both user messages and AI responses along with any tool calls.
-
Contextual Awareness: The AI can now reference previous parts of the conversation, remember what it has already told the user, and build upon earlier tool executions.
-
Session Management: Each chat session is isolated, allowing users to have multiple conversations without cross-contamination of context.
Update the ChatController to support persistent contexts
Update app/Http/Controllers/ChatController.php:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\AIAgent\Tools\ToolUserCreate;
use App\AIAgent\Tools\ToolUserFind;
use App\AIAgent\Tools\ToolUsersList;
use App\AIAgent\Tools\ToolRegistry;
use App\Models\Context;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Log;
use OpenAI\Laravel\Facades\OpenAI;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Response;
class ChatController extends Controller
{
public function newChatContext()
{
return response()->json([
'message' => 'New chat context created',
'chatId' => Context::create(['messages' => []])->id
])->setStatusCode(201);
}
public function streamChat(Request $request, Context $context)
{
// Validate the request
$request->validate([
'message' => 'required|string|max:1000',
]);
Log::info('Streaming chat initiated', [
'chat_id' => $context->id,
'message' => $request->input('message'),
'messages' => json_encode($context->messages),
]);
// Stream the chat response
return Response::eventStream(function () use ($request, $context) {
$ai = new OpenAI;
$registry = new ToolRegistry();
$registry->add(new ToolUsersList($ai));
$registry->add(new ToolUserFind($ai));
$registry->add(new ToolUserCreate($ai));
// Add tools to the OpenAI chat request
$tools = $registry->toOpenAIToolsArray();
// the user and assistant messages
$messages = $context->messages ?? [];
$messages[] = ['role' => 'user', 'content' => $request->input('message')];
// Create a streamed chat response using OpenAI
$response = OpenAI::chat()->create([
'model' => 'gpt-4.1-mini',
'messages' => $messages,
'tools' => $tools,
'tool_choice' => 'auto', // Automatically choose the best tool
]);
Log::info('Chat response received', [
'response' => $response->toArray(),
]);
foreach ($response->choices as $choice) {
if ($choice->message?->content) {
// Add the assistant's message to the messages array
$messages[] = [
'role' => 'assistant',
'content' => $choice->message->content,
];
// Yield the assistant's message content
yield [
'role' => 'assistant',
'delta' => [
'content' => $choice->message->content . PHP_EOL . PHP_EOL,
],
'content' => $choice->message->content . PHP_EOL . PHP_EOL,
];
}
foreach ($choice->message->toolCalls as $call) {
$toolName = $call->function->name;
$arguments = json_decode($call->function->arguments, true, 512, JSON_THROW_ON_ERROR);
$tool = $registry->get($toolName);
yield [
'role' => 'assistant',
'delta' => [
'content' => $tool->getDescription() . PHP_EOL . PHP_EOL
],
'content' => $tool->getDescription() . PHP_EOL . PHP_EOL,
];
$result = $tool->execute($arguments, $ai);
Log::info("Tool executed: {$toolName}", [
'arguments' => $arguments,
'result' => $result,
]);
// add the tool call result to the messages array
$messages[] = [
'role' => $choice->message->role,
'content' => $choice->message->content,
'tool_calls' => [$call->toArray()],
];
// add the result to the messages array
$messages[] = [
'role' => 'tool',
'tool_call_id' => $call->id,
'content' => json_encode($result, JSON_UNESCAPED_UNICODE),
];
// 👇 Send the tool's result back into the chat so the model can continue
$assistantResponse = OpenAI::chat()->create([
'model' => 'gpt-4.1-mini',
'messages' => $messages,
]);
foreach ($assistantResponse->choices as $assistantChoice) {
if ($assistantChoice->message?->content !== null) {
// Add the assistant's message to the messages array
$messages[] = [
'role' => 'assistant',
'content' => $assistantChoice->message->content,
];
yield [
'role' => 'assistant',
'delta' => [
'content' => $assistantChoice->message->content . PHP_EOL . PHP_EOL,
],
'content' => $assistantChoice->message->content . PHP_EOL . PHP_EOL,
];
}
}
}
}
// Update the context with the new messages
$context->messages = $messages;
$context->save();
});
}
}
Update the routes to support chat contexts
The new /chat/new POST route creates a fresh chat session and returns a unique chat ID. The /chat/{context} GET route now accepts a context parameter (the chat UUID) along with the message query parameter, allowing the AI to maintain conversation history across multiple requests.
Update routes/web.php:
<?php
use App\Http\Controllers\ChatController;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
use Inertia\Inertia;
Route::get('/', function () {
return Inertia::render('Chat');
});
Route::post('/chat/new', [ChatController::class, 'newChatContext'])->name('chat.new');
Route::get('/chat/{context}', [ChatController::class, 'streamChat'])->name('chat');
Update the frontend to support persistent contexts
The Chat component now creates a new chat session when the component mounts and maintains the chat context ID in state. The Agent component handles the streaming of responses from the server, updating the running history as each chunk arrives.
The frontend Chat component has been completely redesigned to create an authentic chat interface that mimics modern messaging applications.
New State Management
The Chat component now manages several pieces of state to handle persistent conversations:
chatContextId: Stores the unique UUID for the current chat session, allowing the backend to maintain conversation historymessages: Tracks all user inputs in the current sessioncurrentMessage: Manages the current input field valueloading: Indicates when a new chat session is being created
Chat Context Creation
When the component first mounts, it automatically creates a new chat session by calling the /chat/new endpoint. This returns a unique chat context ID that will be used for all subsequent messages in this conversation.
Chat-Like UI Design
The interface has been transformed from a simple form into a proper chat interface:
Message History Display: Instead of just showing the latest response, the UI now maintains a scrollable chat history that displays all previous messages in chronological order. Each message is clearly distinguished between user and assistant roles.
Message Bubbles: Messages are styled as distinct bubbles with different visual treatments.
Streaming Response Integration
The Agent component handles real-time streaming responses, updating the chat interface as content arrives chunk by chunk. This creates a natural typing effect where users can see the AI’s response appearing in real-time, similar to how human typing would appear in a chat application.
Update resources/js/pages/Chat.tsx:
import { Button } from "@/components/ui/button";
import { Card, CardContent, CardHeader, CardTitle } from "@/components/ui/card";
import { useEventStream } from "@laravel/stream-react";
import axios from "axios";
import { Loader2Icon } from "lucide-react";
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import Markdown from "react-markdown";
/**
* Agent component that handles streaming responses from the server
* @param message - The user message to send to the agent
*/
function Agent({
message,
chatContextId,
}: {
message: string;
chatContextId: string;
}) {
// Store the accumulated response content as it streams in
const [runningHistory, setRunningHistory] = useState<string[]>([]);
// Track whether the agent is currently processing a request
const [isRunning, setIsRunning] = useState(false);
// Set up event stream connection to the Laravel backend
useEventStream(route("chat", { context: chatContextId, message }), {
// Handle stream errors
onError: (error: Event) => {
console.error("Error in event stream:", error);
setIsRunning(false);
},
// Handle stream completion
onComplete: () => {
setIsRunning(false);
},
// Handle incoming messages from the stream
onMessage: (message: MessageEvent) => {
setIsRunning(true);
const data = JSON.parse(message.data);
console.log("Received message:", data.delta);
// Append new content to the running history if it exists
if (data?.delta?.content?.length) {
setRunningHistory((prev) => {
const newHistory = [...prev, data.delta.content];
return newHistory;
});
}
},
});
return (
<div className="mt-4 w-full">
{/* Show the message from the user */}
<div className="flex w-full justify-end">
<div className="mb-2 w-5/6 rounded bg-blue-100 p-2">
<div className="font-bold">User:</div>
<div className="mb-2">{message}</div>
</div>
</div>
{/* Show the agent's response */}
<div className="mb-2 w-5/6 rounded bg-gray-100 p-2">
<div className="font-bold">Agent:</div>
{/* Show loading spinner while agent is running */}
{/* Display the accumulated response with pulse animation while loading */}
<div
className={`prose max-w-none ${isRunning ? "animate-pulse" : ""}`}
>
<Markdown>{runningHistory.join("")}</Markdown>
<div>
{isRunning && (
<Loader2Icon className="size-5 animate-spin" />
)}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
/**
* Main chat component that manages multiple agent conversations
*/
function Chat() {
// Store all active agent instances
const [agents, setAgents] = useState<{ id: number; message: string }[]>([]);
// Counter for generating unique agent IDs
const [nextId, setNextId] = useState(0);
// Current user input message
const [userMessage, setUserMessage] = useState("");
// Chat context id
const [chatContextId, setChatContextId] = useState<string>("");
// Create a new chat context
const createChatContext = async () => {
const response = await axios.post("/chat/new", {
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
});
setChatContextId(response.data.chatId);
setAgents([]); // Reset agents for new chat context
setNextId(0); // Reset agent ID counter
setUserMessage(""); // Clear user message input
console.log("New chat context created:", response.data.chatId);
};
useEffect(() => {
// Create a new chat context when the component mounts
createChatContext();
}, []);
/**
* Create a new agent instance with the given message
* @param message - The message to send to the new agent
*/
const newAgent = (message: string) => {
const agentId = nextId;
setNextId((prev) => prev + 1);
setAgents((prev) => [...prev, { id: agentId, message }]);
};
/**
* Handle form submission to create a new agent conversation
*/
const handleFormSubmit = (e: React.FormEvent<HTMLFormElement>) => {
e.preventDefault();
newAgent(userMessage);
setUserMessage(""); // Clear input after sending
};
return (
<div className="container mx-auto p-4">
<Card>
<CardHeader>
<CardTitle>
<div className="flex items-center justify-between gap-2">
<span>Agentic Chat Session: {chatContextId}</span>
<Button
onClick={createChatContext}
disabled={!chatContextId}
>
New Chat
</Button>
</div>
</CardTitle>
</CardHeader>
<CardContent>
{/* Message input form */}
<form onSubmit={handleFormSubmit}>
<input
type="text"
value={userMessage}
onChange={(e) => setUserMessage(e.target.value)}
placeholder="Type your message here..."
className="mb-2 w-full border p-2"
/>
<Button
type="submit"
disabled={!userMessage.trim() || !chatContextId}
>
Send Message
</Button>
</form>
{/* Render all active agent conversations */}
{agents.map((agent) => (
<Agent
key={agent.id}
message={agent.message}
chatContextId={chatContextId}
/>
))}
</CardContent>
</Card>
</div>
);
}
export default Chat;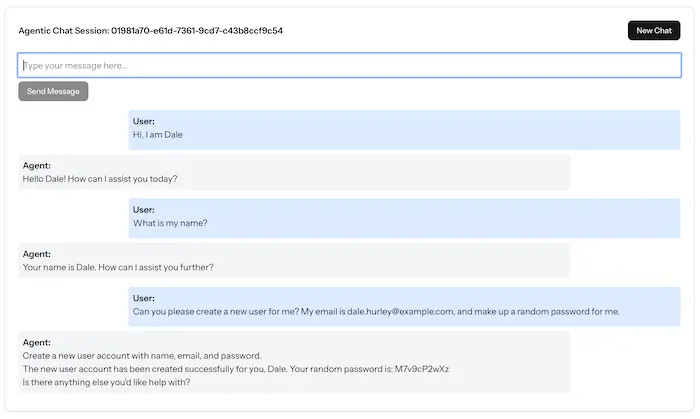
Now your agent has memory! Try this sequence:
- “Create a user named Alice”
- “Now find that user I just created”
- “Create two more users with random names”
- “Show me all the users”
The agent remembers Alice and can build on previous interactions. This is where agentic AI starts to feel truly powerful.
The final solution for Part 4 is available in the ai-agent-tutorial repository on GitHub.
Let’s move on to Part 5: Implementing Automated Planning
Building an Agentic AI Agent Series




