Part 3: Building Custom AI Tools in Laravel & React
Here’s where things get really interesting. Instead of just chatting, we’re going to give our AI agent actual tools it can use to interact with our application.
We’ll build a simple user management system that the AI can control. The agent will be able to create users, find them, and list them—all through natural language commands, e.g. “Create a new user with the name ‘John Doe’ and email ‘john.doe@example.com’ and password ‘password123’”.
You’ll learn how to:
We are following on from Part 2: Streaming Responses with Laravel Stream React and the code from part 2 is available in the ai-agent-tutorial repository on GitHub.
Creating the Tool Infrastructure
The tool infrastructure is the foundation of our AI agent, by definding how tools are structured to best to communicate with the AI and the user. We will be using the OpenAI Function Calling feature to call our tools.
Create the Tool Interface (Optional)
Our first step is to create a consistent structure for our tools. This interface defines how tools communicate with the AI.
Why use an interface?
While interfaces are optional in PHP, using one here ensures all our tools have the same methods and helps catch errors early. It also makes our code more maintainable—when someone creates a new tool, they’ll know exactly what methods to implement. Plus, if we decide to add new properties or methods to our tools in the future, we can update the interface and all implementing classes will be forced to adopt the changes.
Run the following command to create the tool interface:
php artisan make:class AIAgent/Tools/ToolInterfaceUpdate app/AIAgent/Tools/ToolInterface.php:
<?php
namespace App\AIAgent\Tools;
use OpenAI\Laravel\Facades\OpenAI;
interface ToolInterface
{
/** A short, unique identifier (snake_case). */
public function getName(): string;
/** Free-text summary shown to the model / user. */
public function getDescription(): string;
/**
* JSON-Schema describing the arguments the tool accepts.
* Return as a nested assoc-array
*
* Example:
* [
* 'type' => 'object',
* 'properties' => [
* 'query' => ['type' => 'string', 'description' => 'Search phrase'],
* ],
* 'required' => ['query'],
* ]
*/
public function getParameters(): array;
/**
* JSON-Schema describing the output of the tool for the AI model.
* Return as a nested assoc-array.
*
* Example:
* [
* 'type' => 'object',
* 'properties' => [
* 'results' => ['type' => 'array', 'items' => ['type' => 'string']],
* ],
* ]
*/
public function getOutputSchema(): array;
/**
* Execute the tool after the model calls it.
*
* @param array $arguments Validated arguments from the model
* @param OpenAI $AI Shared OpenAI PHP client
* @return mixed Any serialisable result to feed back to the model
*/
public function execute(array $arguments, OpenAI $AI): mixed;
}
Create the Abstract Tool base class (Optional)
Create the abstract tool base class to provide a default implementation for all tools.
Why use an abstract class?
Abstract classes are a great way to enforce a consistent structure for our tools. They provide a base class that concrete tools can extend, and they can override the methods to provide their own implementation. In our examples we are not using the using the full power of the abstract class, but it’s a good practice to use it. For example we might add a new method to the abstract class which then provides a default implementation for all tools.
Run the following command to create the abstract tool base class:
php artisan make:class AIAgent/Tools/AbstractToolUpdate app/AIAgent/Tools/AbstractTool.php:
<?php
namespace App\AIAgent\Tools;
use OpenAI\Laravel\Facades\OpenAI;
/**
* Implement boiler-plate so concrete tools only override what matters.
*/
abstract class AbstractTool implements ToolInterface
{
protected readonly OpenAI $AI;
public function __construct(OpenAI $AI)
{
$this->AI = $AI;
}
/** */
public function getName(): string
{
return 'missing_name';
}
/** By default, no parameters (override in subclass). */
public function getParameters(): array
{
return ['type' => 'object', 'properties' => []];
}
/** By default, no output schema (override in subclass). */
public function getOutputSchema(): array
{
return ['type' => 'object', 'properties' => []];
}
/** Fallback executor (override for real work). */
public function execute(array $arguments, OpenAI $AI): mixed
{
return ['message' => 'Not implemented'];
}
}
Build the Tool Registry
The ToolRegistry is the central manager that orchestrates all our AI tools. It serves three key purposes:
1. Tool Collection & Organization
- Stores all available tools in a keyed array (
$tools) - Provides simple
add()andget()methods for registration and retrieval - Each tool is indexed by its unique name for fast lookups
2. Iteration Support
- Implements
IteratorAggregateso you can loop through tools withforeach - This makes it easy to perform bulk operations on all registered tools
3. OpenAI Format Conversion
- The
toOpenAIToolsArray()method is crucial - it transforms our tool objects into the exact JSON structure that OpenAI’s API expects - Each tool becomes a function definition with name, description, and parameter schema
- This abstraction means we can work with clean PHP objects internally while still meeting OpenAI’s requirements
Think of it as a translator between our PHP tool system and OpenAI’s function calling protocol.
Create the tool registry:
php artisan make:class AIAgent/Tools/ToolRegistryUpdate app/AIAgent/Tools/ToolRegistry.php:
<?php
namespace App\AIAgent\Tools;
class ToolRegistry implements \IteratorAggregate
{
/** @var ToolInterface[] */
private array $tools = [];
public function add(ToolInterface $tool): self
{
$this->tools[$tool->getName()] = $tool;
return $this;
}
public function get(string $name): ?ToolInterface
{
return $this->tools[$name] ?? null;
}
/** Needed for foreach ($registry as $tool) { … } */
public function getIterator(): \Traversable
{
return new \ArrayIterator($this->tools);
}
/**
* Convert all registered tools into the structure expected by
* `chat()->create(['tools' => …])`.
*/
public function toOpenAIToolsArray(): array
{
$out = [];
foreach ($this->tools as $tool) {
$out[] = [
'type' => 'function',
'function' => [
'name' => $tool->getName(),
'description' => $tool->getDescription(),
'parameters' => $tool->getParameters(),
],
];
}
return $out;
}
}
Creating the Tools
Now the basic tool infrastructure is created, we can start creating our tools.
Create the User Creation Tool
The ToolUserCreate allows the AI agent to create new user accounts. The key functions are:
getName(): Returns the tool identifier “create_user” for OpenAI’s function callinggetDescription(): Provides a human-readable and AI-friendly explanation of what the tool doesgetParameters(): Defines the JSON schema for required inputs (name, email, password) for the AI to usegetOutputSchema(): Defines the JSON schema for the output of the tool for the AI model - this will help the AI understand the output of the tool and how to use it when the agent is planning its next stepexecute(): Validates the input data and creates the actual User model in the database
php artisan make:class AIAgent/Tools/ToolUserCreateUpdate app/AIAgent/Tools/ToolUserCreate.php:
<?php
namespace App\AIAgent\Tools;
use App\Models\User;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Hash;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Validator;
use OpenAI\Laravel\Facades\OpenAI;
class ToolUserCreate extends AbstractTool
{
/**
* Get the name of the tool.
*/
public function getName(): string
{
return 'create_user';
}
/**
* Get a description of the tool.
*/
public function getDescription(): string
{
return 'Create a new user account with name, email, and password.';
}
/**
* Get the parameters required by this tool.
*/
public function getParameters(): array
{
return [
'type' => 'object',
'properties' => [
'name' => [
'type' => 'string',
'description' => 'The full name of the user',
'minLength' => 1,
'maxLength' => 255,
],
'email' => [
'type' => 'string',
'description' => 'The email address for the user account',
'format' => 'email',
],
'password' => [
'type' => 'string',
'description' => 'The password for the user account',
'minLength' => 8,
],
],
'required' => ['name', 'email', 'password'],
];
}
public function getOutputSchema(): array
{
return [
'type' => 'object',
'properties' => [
'success' => [
'type' => 'boolean',
'description' => 'Whether the user was created successfully',
],
'user' => [
'type' => 'object',
'properties' => [
'id' => ['type' => 'integer', 'description' => 'User ID'],
'name' => ['type' => 'string', 'description' => 'User name'],
'email' => ['type' => 'string', 'description' => 'User email'],
'created_at' => ['type' => 'string', 'description' => 'Account creation timestamp'],
'updated_at' => ['type' => 'string', 'description' => 'Last update timestamp'],
],
'required' => ['id', 'name', 'email'],
],
'message' => [
'type' => 'string',
'description' => 'Status message or error details',
],
'errors' => [
'type' => 'object',
'description' => 'Validation errors if any',
'additionalProperties' => [
'type' => 'array',
'items' => ['type' => 'string'],
],
],
],
'required' => ['success', 'message'],
];
}
/**
* Execute the tool to create a new user.
*
* @param array $arguments Validated arguments from the model
* @param OpenAI $AI Shared OpenAI PHP client
* @return mixed Any serialisable result to feed back to the model
*/
public function execute(array $arguments, OpenAI $AI): mixed
{
// Validate the input data
$validator = Validator::make($arguments, [
'name' => 'required|string|max:255',
'email' => 'required|string|email|max:255|unique:users',
'password' => 'required|string|min:8',
]);
if ($validator->fails()) {
return [
'success' => false,
'message' => 'Validation failed',
'errors' => $validator->errors()->toArray(),
];
}
try {
// Create the user
$user = User::create([
'name' => $arguments['name'],
'email' => $arguments['email'],
'password' => Hash::make($arguments['password']),
]);
return [
'success' => true,
'user' => [
'id' => $user->id,
'name' => $user->name,
'email' => $user->email,
'created_at' => $user->created_at->toISOString(),
'updated_at' => $user->updated_at->toISOString(),
],
'message' => "User '{$user->name}' created successfully with ID {$user->id}",
];
} catch (\Exception $e) {
return [
'success' => false,
'message' => 'Failed to create user: ' . $e->getMessage(),
];
}
}
}Create the User Listing Tool
The ToolUsersList allows the AI agent to retrieve a list of users from the database.
php artisan make:class AIAgent/Tools/ToolUsersListUpdate app/AIAgent/Tools/ToolUsersList.php:
<?php
namespace App\AIAgent\Tools;
use App\Models\User;
use OpenAI\Laravel\Facades\OpenAI;
class ToolUsersList extends AbstractTool
{
/**
* Get the name of the tool.
*/
public function getName(): string
{
return 'get_the_users';
}
/**
* Get a description of the tool.
*/
public function getDescription(): string
{
return 'Retrieve the user\'s information.';
}
/**
* Get the parameters required by this tool.
*/
public function getParameters(): array
{
return [
'type' => 'object',
'properties' => [
'limit' => [
'type' => 'integer',
'description' => 'The maximum number of users to retrieve',
],
],
'required' => ['limit'],
];
}
public function getOutputSchema(): array
{
return [
'type' => 'object',
'properties' => [
'users' => [
'type' => 'array',
'items' => [
'type' => 'object',
'properties' => [
'id' => ['type' => 'integer', 'description' => 'User ID'],
'name' => ['type' => 'string', 'description' => 'User name'],
'email' => ['type' => 'string', 'description' => 'User email'],
],
'required' => ['id', 'name', 'email'],
],
],
],
];
}
/**
* Execute the tool to retrieve users.
*
* @param array $arguments Validated arguments from the model
* @param OpenAI $AI Shared OpenAI PHP client
* @return mixed Any serialisable result to feed back to the model
*/
public function execute(array $arguments, OpenAI $AI): mixed
{
$limit = $arguments['limit'] ?? 10; // Default to 10 if not provided
$users = User::select('id', 'name', 'email')
->limit($limit)
->get()
->toArray();
return [
'users' => $users,
];
}
}
Create the User Search Tool
The ToolUserFind allows the AI agent to find a specific user by their ID or email address.
php artisan make:class AIAgent/Tools/ToolUserFindUpdate app/AIAgent/Tools/ToolUserFind.php:
<?php
namespace App\AIAgent\Tools;
use App\Models\User;
use OpenAI\Laravel\Facades\OpenAI;
class ToolUserFind extends AbstractTool
{
/**
* Get the name of the tool.
*/
public function getName(): string
{
return 'find_user';
}
/**
* Get a description of the tool.
*/
public function getDescription(): string
{
return 'Find a specific user by their ID or email address.';
}
/**
* Get the parameters required by this tool.
*/
public function getParameters(): array
{
return [
'type' => 'object',
'properties' => [
'id' => [
'type' => 'integer',
'description' => 'The user ID to search for',
],
'email' => [
'type' => 'string',
'description' => 'The email address to search for',
],
],
'required' => [],
];
}
public function getOutputSchema(): array
{
return [
'type' => 'object',
'properties' => [
'success' => [
'type' => 'boolean',
'description' => 'Whether the user was found',
],
'user' => [
'type' => 'object',
'properties' => [
'id' => ['type' => 'integer', 'description' => 'User ID'],
'name' => ['type' => 'string', 'description' => 'User name'],
'email' => ['type' => 'string', 'description' => 'User email'],
'email_verified_at' => ['type' => ['string', 'null'], 'description' => 'Email verification timestamp'],
'created_at' => ['type' => 'string', 'description' => 'Account creation timestamp'],
'updated_at' => ['type' => 'string', 'description' => 'Last update timestamp'],
],
'required' => ['id', 'name', 'email'],
],
'message' => [
'type' => 'string',
'description' => 'Status message',
],
],
'required' => ['success', 'message'],
];
}
/**
* Execute the tool to find a user.
*
* @param array $arguments Validated arguments from the model
* @param OpenAI $AI Shared OpenAI PHP client
* @return mixed Any serialisable result to feed back to the model
*/
public function execute(array $arguments, OpenAI $AI): mixed
{
$user = null;
// Search by ID if provided
if (isset($arguments['id'])) {
$user = User::find($arguments['id']);
$searchType = 'ID ' . $arguments['id'];
}
// Search by email if provided (and ID not provided)
elseif (isset($arguments['email'])) {
$user = User::where('email', $arguments['email'])->first();
$searchType = 'email ' . $arguments['email'];
} else {
return [
'success' => false,
'message' => 'Either ID or email must be provided',
];
}
if ($user) {
return [
'success' => true,
'user' => [
'id' => $user->id,
'name' => $user->name,
'email' => $user->email,
'email_verified_at' => $user->email_verified_at?->toISOString(),
'created_at' => $user->created_at->toISOString(),
'updated_at' => $user->updated_at->toISOString(),
],
'message' => "User found with {$searchType}",
];
}
return [
'success' => false,
'message' => "No user found with {$searchType}",
];
}
}Wire the tools into the ChatController
Now for the magic—connecting everything together. This is where our tool registry pattern and OpenAI’s function calling capabilities merge to create a dynamic AI agent system.
The ChatController serves as the orchestrator, instantiating our ToolRegistry and registering each tool we’ve built. When a user sends a message, OpenAI analyzes the intent and automatically selects the appropriate tool(s) to fulfill the request. If the AI determines it needs to create a user, it calls our ToolUserCreate; if it needs to find a user, it uses ToolUserFind; and if it needs to list users, it leverages ToolUsersList.
The beauty of this architecture is its extensibility—adding new capabilities is as simple as creating a new tool class and registering it. The AI agent can chain multiple tool calls together, handle errors gracefully, and provide meaningful responses back to the user, all while maintaining a clean separation of concerns between the AI orchestration layer and our business logic.
Update the ChatController to use the tools
Update app/Http/Controllers/ChatController.php:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\AIAgent\Tools\ToolUserCreate;
use App\AIAgent\Tools\ToolUserFind;
use App\AIAgent\Tools\ToolUsersList;
use App\AIAgent\Tools\ToolRegistry;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Log;
use OpenAI\Laravel\Facades\OpenAI;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Response;
class ChatController extends Controller
{
public function streamChat(Request $request)
{
return Response::eventStream(function () use ($request) {
$ai = new OpenAI;
$registry = new ToolRegistry();
$registry->add(new ToolUsersList($ai));
$registry->add(new ToolUserFind($ai));
$registry->add(new ToolUserCreate($ai));
// Add tools to the OpenAI chat request
$tools = $registry->toOpenAIToolsArray();
// Create a streamed chat response using OpenAI
$response = OpenAI::chat()->create([
'model' => 'gpt-4.1-mini',
'messages' => [
['role' => 'user', 'content' => $request->input('message')],
],
'tools' => $tools,
'tool_choice' => 'auto', // Automatically choose the best tool
]);
Log::info('Chat response received', [
'response' => $response->toArray(),
]);
foreach ($response->choices as $choice) {
if ($choice->message?->content) {
yield [
'role' => 'assistant',
'delta' => [
'content' => $choice->message->content . PHP_EOL . PHP_EOL,
],
'content' => $choice->message->content . PHP_EOL . PHP_EOL,
];
}
foreach ($choice->message->toolCalls as $call) {
$toolName = $call->function->name;
$arguments = json_decode($call->function->arguments, true, 512, JSON_THROW_ON_ERROR);
$tool = $registry->get($toolName);
yield [
'role' => 'assistant',
'delta' => [
'content' => $tool->getDescription() . PHP_EOL . PHP_EOL
],
'content' => $tool->getDescription() . PHP_EOL . PHP_EOL,
];
$result = $tool->execute($arguments, $ai);
Log::info("Tool executed: {$toolName}", [
'arguments' => $arguments,
'result' => $result,
]);
// 👇 Send the tool's result back into the chat so the model can continue
$assistantResponse = OpenAI::chat()->create([
'model' => 'gpt-4.1-mini',
'messages' => [
// Include the original message and the tool call result
['role' => 'user', 'content' => $request->input('message')],
[
'role' => $choice->message->role,
'content' => $choice->message->content,
'tool_calls' => [$call->toArray()],
],
[
'role' => 'tool',
'tool_call_id' => $call->id,
'content' => json_encode($result, JSON_UNESCAPED_UNICODE),
],
],
]);
foreach ($assistantResponse->choices as $assistantChoice) {
if ($assistantChoice->message?->content !== null) {
yield [
'role' => 'assistant',
'delta' => [
'content' => $assistantChoice->message->content . PHP_EOL . PHP_EOL,
],
'content' => $assistantChoice->message->content . PHP_EOL . PHP_EOL,
];
}
}
}
}
});
}
}
Seed some test data
Let’s create some users to work with:
Update database/seeders/DatabaseSeeder.php:
<?php
namespace Database\Seeders;
use App\Models\User;
// use Illuminate\Database\Console\Seeds\WithoutModelEvents;
use Illuminate\Database\Seeder;
class DatabaseSeeder extends Seeder
{
/**
* Seed the application's database.
*/
public function run(): void
{
User::factory(10)->create();
}
}
Run the following command to seed the database:
php artisan db:seedNow for the magic moment. Visit http://localhost:8000/ and try these commands:
- “Create a new user with random details”
- “Get 100 of the users”
- “Find the user with ID 1”
- “Create a user named John Doe with email john@example.com”
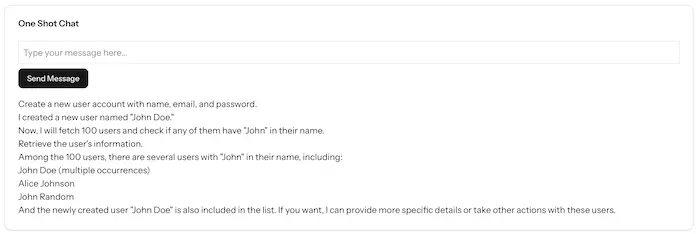
You’ve just built an AI that can actually do things, not just talk about them. The AI understands your natural language request, chooses the appropriate tool, executes it, and reports back with the results. This is the core of agentic behavior.
The final solution for Part 3 is available in the ai-agent-tutorial repository on GitHub.
Let’s move on to Part 4: Adding Stateful Context to Your Agent
Building an Agentic AI Agent Series




